|
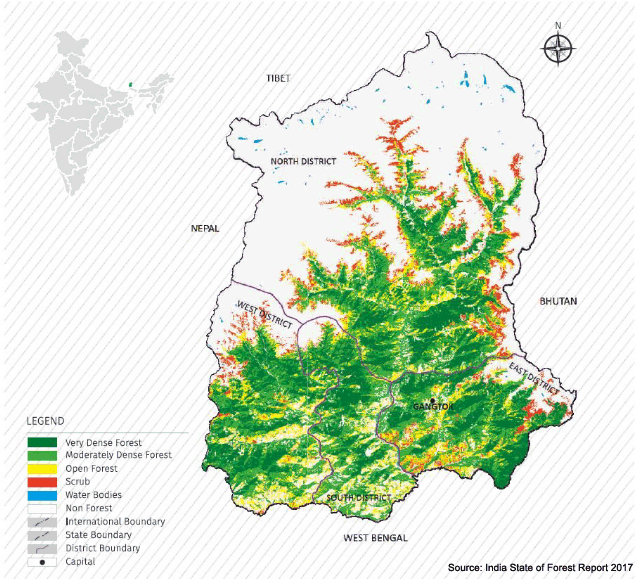
Forest is one of the richest natural resources of Sikkim. With luxuriant forest abounding in all part of state, Forestry has been the major land use in the State and 82.31% of the total geographical area of the State is under the administrative control of the State Forest Department. The total Forest Cover of the State as per the latest Indian State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2023 is 3358.40 sq. km (47.33%) of the total geographical area of the state) and tree cover is 48.33 sq km. The total Forest and Tree Cover accounts to 3406.73 sq.km (48.01%) of the total geographical area of the state. The composition ranges from tropical Dry Deciduous Forests with Sal and its associates in the valleys of Teesta and Rangit to the Alpine Scrub and grassland in high altitude.
Note: In the State of Sikkim about 44 % of total geographical area is under Alpine pasture & scrub and under perpetual snow cover. Hence, in these areas, it would not be possible to bring the tree cover. The area considered for the tree cover may therefore be excluding these areas. |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Sikkim Forest Statistics (Source: Indian State of Forest Report - Forest Survey of India)
Forest Types of Sikkim
Forest Management
Strengthening of
Territorial Sector: Forrest Management and Protection are the dual functions of this sector. The
Government has addressed these vital issues in recent years than ever before in
politically sensitive way. A motivated field staff, sound legal enactment,
efficient & effective transport and communication, accommodation facilities,
self defence and uniforms, etc. are some of the pre-requisites to accomplish the
effective management and protection.
Grazing control: The Government has imposed a ban on grazing within the Reserve Forest, Plantation areas and Water sources areas with a view to encourage regeneration of forest resources, augment rural water supplies and develop degraded lands. The beneficial effects of this policy are already manifested in the form of improved supplies of water in the villages bordering the Forest areas, regeneration of degraded forest land and enhancement if overall natural resources status. A number of Gots have been removed and the cattle have been impounded & fined along with the wide publicity & awareness. Joint Forest Management Committees (JFMC’s) & FDA: The policy of the Government to decentralize powers and functions to the grassroots levels has also been extended to the territorial and wildlife sectors. The Government has adopted the participatory approach to forest protection, management and development. It has taken up formation of Joint Forest Management Committees / Eco-Development Committees at the village-level which comprises of all the villagers who wish to participate in the forest management, development and protection functions of the forests that are located in the vicinity of their villages. So far 155 JFMC’s (Under four territorial FDAs) have been registered all over the State and the work of JFMC constitution in the villages not yet covered. At the district level all the JFMC’s have together been formed into a confederation called the Forest Development Agency (FDA). The JFMC’s will be entrusted with the task of afforestation and protection of the natural resources of their area and they will be implementing the National Afforestation Programme through the four FDAs in the Tenth Plan period. More than 10000 hectares of land will be developed over the Plan period through this Scheme. Infrastructure Development (Buildings): The Government has been developing infrastructural facilities for the Forest, Environment & Wildlife management staff with Central as well as State assistance in order to modernize its management and protection functions. At Gangtok Transit Hostel, Repair of road, quarter has been completed. Divisional Forest Officer quarters/office(4), Assistant Conservator of Forest quarters(4), RO quarters(6), BO quarters(12), FG quarters(30) and Check posts(3) have been completed during the period 2002-03-04. Infrastructure Development (Wireless Communication & Arms/ Ammunition): The wireless communication has been strengthened further. Almost State-wide Wireless Networking has been achieved except a few locations like Lachen, Lachung, Lingmoo and a few other areas which are likely to be covered in the next year. Static sets, hand sets mobile sets have been provided to all the field level functionaries for effective communication. In keeping with the requirements of modern policing functions of forest areas the Government has also inducted arms / ammunition to the field level staff. Arms /ammunition have been provided to selected stations. There is need to procure more which may be done in the current year. Arms training was done at SAP headquarter, Pangthang. At present total (W/T): Repeater sets-5 nos, Static sets-43 nos, Hand sets-73 nos. along with accessories, Total (Arms): .22 Rifle -25nos., .315 Rifle- 6nos. and 9mm auto Pistol -9 nos along with ammunition Infrastructure Development (Computerization): Computerizations of important forestry functions have been initiated. Computers have been provided to all the divisions. There is need to provide computer in selected Ranges also. Fax machines have also been provided to all divisions. Survey & Demarcation: The government proposes to take up survey and demarcation of forest areas during the Tenth Plan in order to consolidate the forest resources of the State. In the area Survey and Demarcation of the forest land have been initiated in the systematic manner. The forest areas in Sikkim in the first half of the 20th century had been surveyed and demarcated into Reserves, Khasmal and Gorucharan forests. The forest boundaries then had been demarcated by erecting loose stone mounds. These have subsequently vanished due to the burgeoning population leading to sizable forest area encroachment. In order to determine the exact extent of encroachment resurvey was required. Subsequently to establish the forest boundaries and evict the encroachers resurvey & demarcation by erecting new iron post pillars had commenced from 2001. In the initial phase 72 kms of the forest boundaries was surveyed & demarcated by erecting 223 iron pillar posts at a cost of Rs.8.53 lakhs. However while surveying & demarcating 72 kms, three pillars per km was found insufficient to distinctly demarcate the state’s forest boundaries due to the difficult and undulating terrain spread over remote hilly areas. Hence after obtaining the necessary approval for erecting ten pillars per km, the resurvey & demarcation activities commenced from 2003 wherein108 kms of the forest boundaries were surveyed and demarcated during 2003-04 at an expenditure of Rs.24.90 lakhs. Thus 180 kms of the boundaries have been surveyed and demarcated with 1306 nos of iron pillar posts till date. All the forest boundaries so demarcated till date are of RFs. The spillover of 32 kms at Rs.7.32 lakhs are being undertaken during the CFY i.e 2004-05. However due to the late receipt of the sanction letter for 2003-04 and the change in funding pattern from 100%CSS to 75%:25%; the original target of surveying & demarcating 700 kms of forest boundaries are being taken up in the current year. Transport & Other facilities: Patrolling vehicle with wireless communication system has been provided to all the four Territorial divisions. There is need to have the more patrolling vehicles in sensitive selected ranges like Lachen, Lachung, Singtam, Namthang, Melli, Nayabazar and one in Gangtok for control room. [Top] |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
FOREST AND ENVIRONMENT DEPARTMENT Government of Sikkim
ENVIRONMENT Quick Links: SoE Report |
Pollution |
Status & Issues |
EIA/EMP |
SEIAA/SEAC |
Clearances |
Public Notice |
NEAC |
NGC |
...More
BIODIVERSITY Quick Links: Flora & Fuana |
State Biodiversity Board |
State Biodiversity Rules |
State Biodiversity Action Plan |
Medicinal Plants & NTFP |
IBAs |
Bamboo Species | ...More
WILDLIFE Quick Links: Protected Areas |
Himal Rakshaks |
Conservation Zones |
Prespective Management Strategies |
...More
FOREST & FORESTRY Quick Links: Forest Types of Sikkim |
Forest Management |
Forest Statistics | ...More
LAND & WATER Quick Links: Wetlands |
Wastelands |
Treatment of Landslides & Soil Erosion Control |
Pokhri Sangrakshan Samiti |
...More
ECOTOURISM Quick Links: White Paper on Ecotourim Policy |
Sikkim Trekking Regulation |
Ecotourism Destinations |
Sacred Natural Sites | ...More
SERICULTURE Quick Links: Sericulture Directorate |
Beneficiaries |
Silk Industry |
Eri & Muga Sectors |
Marketing, Infrastructure & Employment




 National Integration
National Integration